Bridge
The StaticMCP Bridge is the critical component that enables standard MCP clients to seamlessly interact with static file-based context servers. Acting as a lightweight translation layer, the bridge converts real-time MCP requests into file system operations, making static pre-generated content appear as a fully dynamic MCP server.
Hosted Bridge Service
URL: https://bridge.staticmcp.com
The easiest way to use StaticMCP is with our hosted bridge service. No servers to run, no infrastructure to manage.
Quick Start
# 1. Deploy your StaticMCP files to any static host
netlify deploy --dir ./your-staticmcp-output
# 2. Connect AI clients to the hosted bridge
https://bridge.staticmcp.com/sse?url=https://your-site.netlify.app
Usage Examples
With MCP Inspector (Testing):
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector \
"https://bridge.staticmcp.com/sse?url=https://your-site.com"
With Claude Desktop:
{
"mcp": {
"servers": {
"my-docs": {
"command": "curl",
"args": [
"-X", "POST",
"https://bridge.staticmcp.com/sse?url=https://your-site.com"
]
}
}
}
}
When to Use Hosted Bridge
- ✅ Quick prototyping - Get started in minutes
When to Self-Host
- 🔧 Custom extensions - Need runtime extensions not in hosted version
- 🔧 Enterprise requirements - Custom SLAs or compliance needs
- 🔧 High volume - Beyond free tier limits
- 🔧 Network restrictions - Must route through private networks
Architecture Role
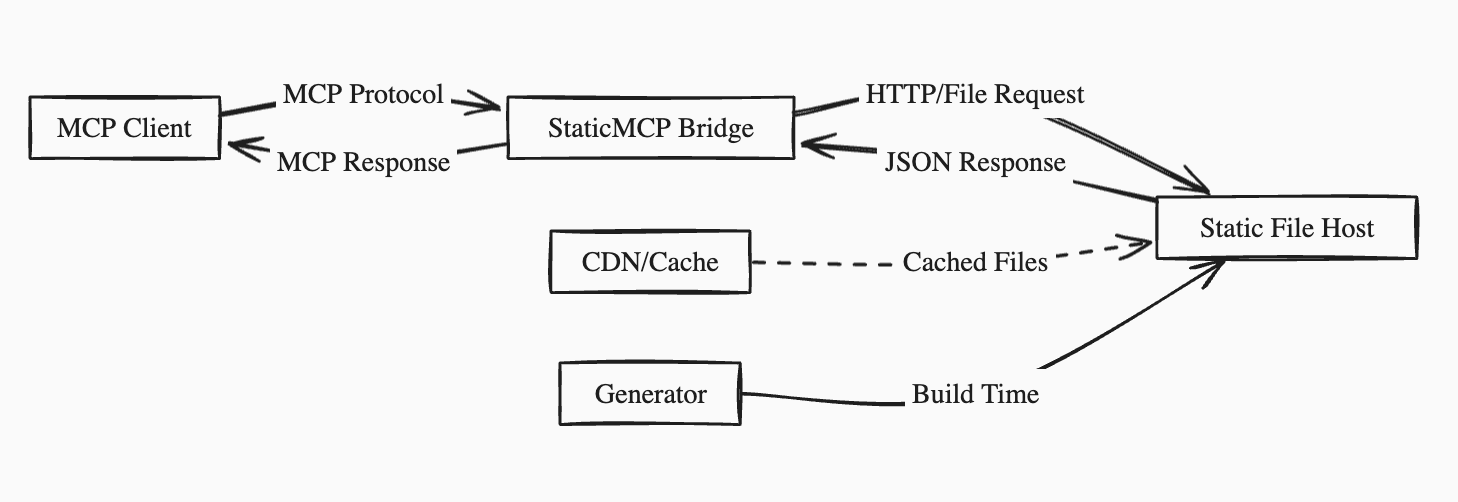
The bridge serves as the interface between two worlds:
- MCP Protocol Side: Handles standard MCP requests from AI models and applications via JSON-RPC over stdio, HTTP, or SSE
- Static File Side: Translates requests into appropriate file paths and HTTP requests
This separation allows StaticMCP to leverage the full power of modern web infrastructure while maintaining complete compatibility with existing MCP tooling.
Transport Support
StaticMCP bridges can implement any of the standard MCP transport mechanisms:
JSON-RPC over Stdio
Traditional command-line bridges that communicate via standard input/output:
- Ideal for development tools and local testing
- Compatible with MCP Inspector and development environments
- Simple process-based isolation and debugging
HTTP Transport
RESTful bridges that expose MCP operations as HTTP endpoints:
- Native web integration for browser-based clients
- Standard HTTP status codes and headers
- Easy integration with existing web infrastructure
- Support for CORS and web security policies
Server-Sent Events (SSE)
Real-time bridges using SSE for bi-directional communication:
- Efficient for long-running connections
- Built-in reconnection and error handling
- Ideal for web applications requiring live updates
- Lower latency than traditional HTTP polling
Core Responsibilities
Protocol Translation
The bridge's primary function is converting MCP operations into file system requests:
- Resource Requests: Map
resources/readcalls to specific JSON files in theresources/directory - Tool Calls: Transform
tools/callrequests into lookups in thetools/hierarchy - Capability Discovery: Serve manifest information from the root
mcp.jsonfile
Request Routing
Bridges implement intelligent routing logic to map complex requests to static files:
MCP Request: resources/read { uri: "file://README.md" }
↓
File Path: resources/README.md.json
↓
HTTP Request: GET https://cdn.example.com/resources/README.md.json
Error Handling
Professional error handling ensures graceful degradation:
- File Not Found: Convert 404 errors into appropriate MCP error responses
- Network Issues: Handle connectivity problems with service unavailable errors
- Invalid Content: Validate JSON responses and handle parsing errors
Caching Integration
Bridges can implement sophisticated caching strategies:
- Local Caching: Store frequently accessed files in memory or local storage
- HTTP Caching: Respect and leverage standard HTTP cache headers
- CDN Integration: Work seamlessly with content delivery networks
Implementation Approaches
Standalone Servers
Independent bridge applications that run as separate processes:
- Stdio Bridges: Accept MCP requests via standard input/output for command-line tools
- Streamable HTTP Servers: Provide single-endpoint HTTP bridges for modern web clients
- Legacy HTTP+SSE Servers: Support deprecated dual-endpoint pattern for backward compatibility
- Handle requests to static file hosts
- Suitable for development and testing environments
- Can be written in any programming language
Embedded Libraries
Bridge functionality integrated directly into MCP client applications:
- Eliminate network overhead between client and bridge
- Enable advanced caching and optimization strategies
- Provide tighter integration with application logic
- Ideal for production deployments
Serverless Functions
Cloud-hosted bridges deployed as serverless functions:
- Automatically scale with demand
- Integrate with cloud storage and CDN services
- Provide geographic distribution for global applications
- Reduce operational overhead
Proxy Services
Bridge services that sit between multiple clients and static hosts:
- Share cached content across multiple MCP clients
- Implement advanced rate limiting and authentication
- Provide monitoring and analytics capabilities
- Support multi-tenant scenarios
Configuration Options
Source Location
Bridges support multiple source types for maximum flexibility:
- Local File System: Direct access to local directories for development
- HTTP/HTTPS URLs: Remote static hosting for production deployments
- Cloud Storage: Integration with AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, etc.
- CDN Endpoints: Direct connection to content delivery networks
Performance Tuning
- Connection Pooling: Reuse HTTP connections for improved performance
- Concurrent Requests: Handle multiple simultaneous requests efficiently
- Timeout Configuration: Appropriate timeouts for different network conditions
- Retry Logic: Intelligent retry strategies for transient failures
Security Features
- HTTPS Enforcement: Ensure secure communication with static hosts
- Access Control: Implement authentication and authorization where needed
- Input Validation: Sanitize requests to prevent security vulnerabilities
- Rate Limiting: Protect against abuse and ensure fair resource usage
Bridge Deployment Options
| Feature | Hosted Bridge | Self-Hosted SSE | Self-Hosted STDIO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setup Time | Instant | 30 minutes | 10 minutes |
| Maintenance | Zero | Medium | Low |
| Custom Extensions | Built-in only | Full support | Full support |
| Global Performance | Excellent | Depends on deployment | Local only |
| Cost | Free (with limits) | Infrastructure cost | Device power |
| Use Case | Production, prototyping | Enterprise, custom needs | Development, testing |
Recommendation: Start with the hosted bridge, then self-host if you need custom extensions or have more powerful demands.
Types
STDIO
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector staticmcp_stdio_bridge ./my-static-mcp/
Checkout stdio_bridge for more details
Fixed SSE
On the hosting server, start the SSE server to host the StaticMCP files (which partially looses the benefit of it being static).
staticmcp_sse_fixed ./my-static-mcp/
staticmcp_sse_fixed https://staticmcp.com/mcp/
Checkout staticmcp_sse_bridge for more details.
Dynamic SSE
Use a dynamic SSE bridge that takes in the url to the StaticMCP files as param.
https://bridge.staticmcp.com/sse?url=https://staticmcp.com/mcp/
Checkout staticmcp_sse_bridge for more details.
Standard Compliance
StaticMCP bridges maintain strict compatibility with MCP specifications across all transport methods:
- Protocol Versions: Support for current MCP protocol versions
- Transport Flexibility: JSON-RPC over stdio, Streamable HTTP, or legacy HTTP+SSE transports
- Message Format: Full compliance with MCP message schemas
- Error Codes: Standard MCP error codes and message formats
- Response Format: Exact adherence to MCP response schemas
This ensures that any MCP client can work with StaticMCP without modification, regardless of the chosen transport mechanism.
Extensions
TBD